Some means to reduce acoustic noise
Several factors are contributing to the performance of the hydroacoustic equipment used on board a vessel. Careful planning of the installation may reduce the acoustic noise.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to simply provide a number of specific procedures to reduce the noise.
An important factor is the physical location of the transducers. This depends on the vessel's design and construction, how the hull is shaped, and how the water runs along the hull. Other factors deal with other equipment mounted on board, and this will also be vessel dependant. At moderate ship speeds the machinery noise is usually dominant. At medium speeds the flow noise increases more rapidly and takes over, while at higher speed the propeller noise will be the
main contributor.
Note
The information here must be considered as general advice. Each system installation must be handled separately depending on the hull design and the other electrical and mechanical systems
installed on the vessel.
Reducing flow noise
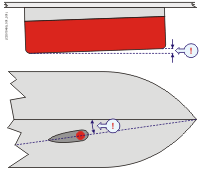
The shape of the transducer (or dome around it) must be as streamlined as possible. The hull plating in front of the transducer must be as smooth as possible.
Important
Be especially aware of bilge keels and sacrificial anodes. The keel must be rounded off without sharp edges. Neither extruding objects nor abrupt transitions must be present.
Each transducer must be mounted with a small inclination angle (approximately 2 degrees).
Reducing machinery noise
| • | Each transducer must be installed as far away from the engine room as possible. |
| • | The main engine and relevant auxiliary engines and equipment must be fixed to rigid foundations to avoid vibrations. |
| • | Any hull structure that may vibrate must be damped or coated to reduce the vibrations. |
The use of shock absorbers or floating rafts may sometimes reduce this noise. The structure-borne noise may be reduced by isolation, for example by providing vibration clamping between the transducer
and the hull structure.
Reducing propeller noise
The transducer must be installed as far away from the propellers as possible. Sufficient clearance between the propellers and the hull, the rudder and the keel must be provided.
Place the sacrificial anodes in places where the water flow is the least disturbed.
Ensure that the propellers blades are correctly designed and without damages. The use of a baffle between the propellers and the transducer may reduce noise appreciably. Static discharges caused by the rotating propeller shaft may be removed by proper grounding or by mounting a coal brush from
the shaft to vessel ground.
Reducing rattle noise
Ensure that no parts near the transducers can rattle as a result of water flow or vibrations.
Reducing interference
Interference from the transmission pulses from other hydroacoustic instruments on board the vessel is difficult to avoid. The problem may be reduced by choosing the working frequencies carefully and to some extent by separating the different transducers. On vessels with a large number of separate hydroacoustic systems installed and in simultaneous use, a separate synchronizing
system (for example the K-Sync) should be considered.
Reducing electrical noise
These points must all be considered to reduce electrical noise on an EK80 system.
| • | Place the transducer cables in a metal conduit all the way from the transducer to the transceiver. Terminate the conduit as close to the transducer and transceiver as possible. |
| • | Make sure that the transducer cables are completely separated from other cables, boxes, other potential noise sources. |
| • | Make sure that all units are properly grounded. |
| • | Use shielded cables with correct grounding. |
| • | Separate the cables used by the EK80 system from other cables with high voltages, large currents or transients. Place all high voltage power cables in metal conduits. |
| • | If you more than one Wide Band Transceiver (WBT), install these in such a way that the transducer cables have the maximum distance to the power and Ethernet cables. |
| • | Ensure maximum physical distance between the transceiver and the power supply. |
| • | Ensure maximum physical distance between each power supply. |
| • | If possible, install the transceivers in a sonar room that is electrically shielded. |