About data subscriptions and remote control
The EK80 Wide band scientific echo sounder allows you subscribe to echo data and to control the operation from your own remote application. In this way you can create your own software for controlling the EK80 operations. Such operations may for example include start/stop pinging, changing ping interval, or start/stop data recording.
By means of your client application you can subscribe to data from the EK80. This means that you can ask the EK80 to continuously send various data (for example Depth data, Target Strength data or Integration data) to your client application.
Note
In this context the EK80 Processor Unit is regarded as the "server". The EK80 program is the "server application". The program you make yourself for running on a local computer is referred to as the "client application".
The communication between the EK80 program and your own client application is done by exchanging UDP messages via the local area network (LAN). Command and response messages are all text messages on XML format. Subscribed data updates are binary data structures. These must be decoded using the relevant information about the data structure.
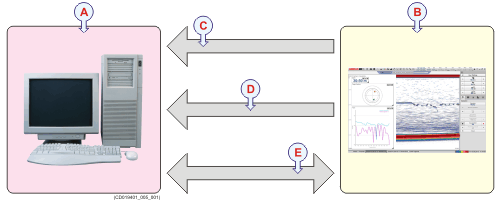
| A | Local computer (normally connected to the local area network) running your own program ("client application"). |
| B | Processor Unit running the EK80 program ("server application"). |
| C | Subscriber parameter updates (UDP/Binary) |
| D | Subscribed data updates (UDP/Binary) |
| E | Commands and responses (UDP/XML) |