Noise page
The operational performance of the EK80 system depends on the noise conditions. It is essential that the noise signature is as low as possible.
How to open
This page is located in the Diagnostics dialog box.
Open the Diagnostics dialog box from the Setup menu.
Description
The Noise page provides information about the current estimated noise, and the equivalent ambient noise. Your EK80 system must be set to Passive mode.
Tip
If you want to switch to Passive mode, use the Normal Operation dialog box. The Normal Operation dialog box is located on the Operation menu.
LFM (Linear Frequency Modulation) transmissions
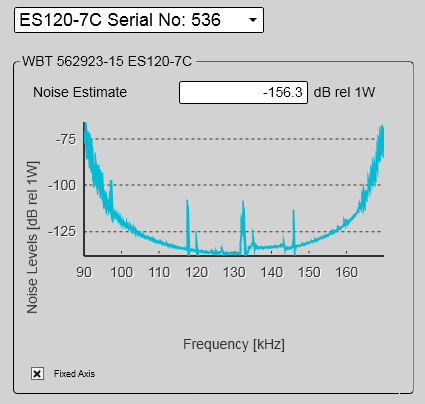
When you work with LFM transmission, the noise can be presented in a plot. The plot shows the noise level as a function of the transmission frequency.
Tip
Select Fixed Axis to make the curves easier to read.
If you wish to switch pulse type between CW and LFM, use the Normal Operation dialog box. Before selecting LFM transmissions, make sure that your EK80 system is provided with a compatible transducer!
(The screen capture has been made while using a dummyload.)
CW (Continuous Wave) transmissions
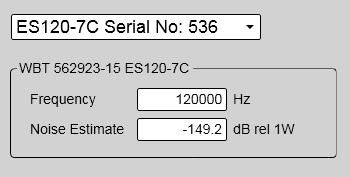
When you work with CW transmissions, the noise is presented in text boxes.
(The screen capture has been made while using a dummyload.)
About noise
The noise that contributes to the signal to noise ratio may be divided into the following types of noise:
| • | Self noise |
| • | Ambient noise |
| • | Electrical noise |
| • | Reverberation |
| • | Underwater noise |
| • | Fishing gear noise |
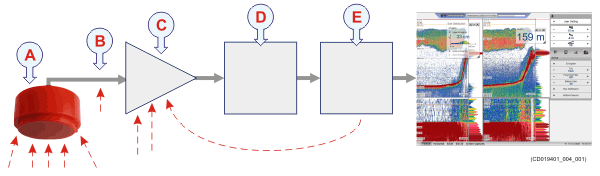
| A | The transducer can pick up noise from:
|
| B | The transducer cable is long. Electric noise from generators, pumps, cooling systems and other electric or electromechanical devices is easily picked up. |
| C | The preamplifiers are very sensitive. They can easily pick up electrical noise from internal and external power supplies. The preamplifiers are also vulnerable to analogue noise created by their own electronic circuitry. Digital noise created by the converter and processing circuitry can also create noise problems. |
| D | The converters transform the analogue echoes to digital format. |
| E | Signal processing circuitry can create digital noise. |
Details
Noise Estimate
Use the spin box to select which channel to study. In this context, the term channel is used as a common term to identify the combination of transceiver, transducer and operating frequency.
Noise Estimate
For every transmission ("ping") the EK80 system measures the echo levels along the chosen range. Typically, these measurements are made every five meters, even for long ranges.
All echoes and noise in the water are recorded. This includes noise generated by your own vessel (electric, propellers, machinery etc), water flow, cavitation and interference. Echoes from fish and other species, as well as from the bottom, are detected and added to the equations.
By comparing these measurements, the EK80 system calculates a noise estimate.
Tip
If you set the EK80 system to Passive mode, all echoes from the transmissions are removed from the equations. This gives you with better information about the
actual noise.
This information is also shown on the Extras "menu".
Equivalent Ambient Noise
The noise estimate provided by the EK80 system includes all noises. This includes noise generated by your own vessel, for example electric noise, propellers, machinery and mechanical vibrations. By means of additional equations, the noise values are compensated for the bandwidth. The equivalent ambient noise value attempts to present the total noise as if it was all from ambient sources.
This information is also shown on the Extras "menu".